Earth Observation Data to Support Environmental Justice: Linking Non-Permitted Poultry Operations to Social Vulnerability Indices
Abstract
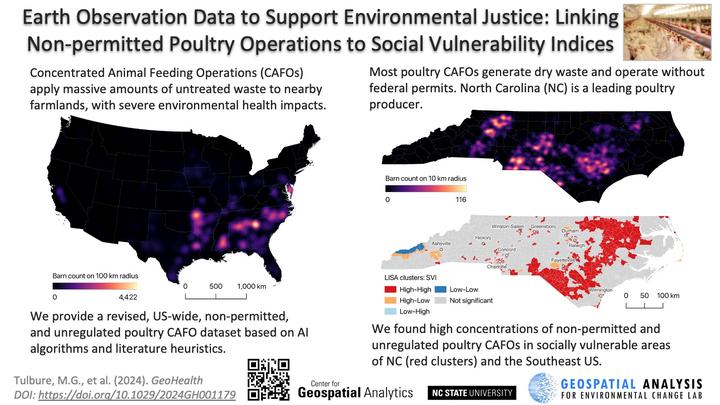
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs) apply massive amounts of untreated waste to nearby farmlands, with severe environmental health impacts of swine CAFOs and proximity to disadvantaged communities well documented in some US regions. Most studies documenting the impacts of CAFOs rely almost exclusively on CAFO locations known from incomplete public records. Poultry CAFOs generate dry waste and operate without federal permits; thus, their environmental justice (EJ) impacts are undocumented. North Carolina (NC), a leading poultry producer, has seen a significant increase in poultry CAFOs, particularly since the 1997 swine CAFO moratorium. Using literature-derived heuristics, this study refined the locations of poultry CAFOs derived based on Earth Observation (EO) data and deep learning, reducing the overestimation of poultry CAFO density by 54% after heuristic adjustments. We removed 51.8% of misclassified features in NC and 61.5% across the US, significantly improving data set accuracy. Spatial analysis, including Local Indicators of Spatial Association, revealed that poultry CAFOs often cluster in census tracts with high Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) scores, indicating potential EJ issues. Notably, one-third of NC’s census tracts with high poultry CAFO density also have high SVI, primarily in rural eastern regions. Similar patterns were observed in the South and Southeast of the US. However, not all high-density CAFO areas correspond with high SVI, suggesting a complex relationship between CAFO locations and community vulnerabilities. This study highlights the critical need for comprehensive, high-quality data on unpermitted poultry CAFOs derived using AI algorithms to fully understand their impacts on communities and accurately inform EJ evaluations.