Spatiotemporal dynamics of surface water networks across a global biodiversity hotspot—implications for conservation
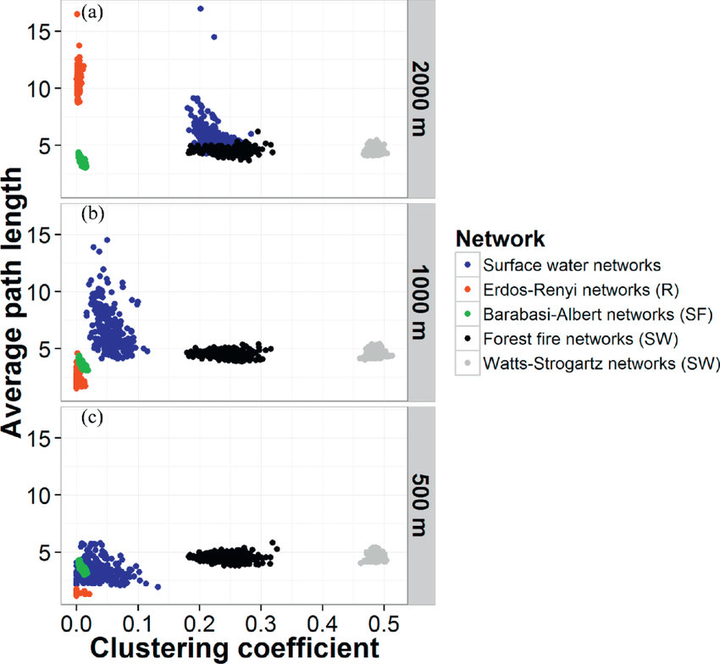 Comparison of surface water networks on the SCP with alternative models such as random (R), scale free (SF) and small-world (SW) networks for key metrics including average minimum path length (y-axis) and clustering coefficient/transitivity (x-axis) at (a) 2000 m; (b) 1000 m and (c) 500 m.
Comparison of surface water networks on the SCP with alternative models such as random (R), scale free (SF) and small-world (SW) networks for key metrics including average minimum path length (y-axis) and clustering coefficient/transitivity (x-axis) at (a) 2000 m; (b) 1000 m and (c) 500 m.Abstract
The concept of habitat networks represents an important tool for landscape conservation and management at regional scales. Previous studies simulated degradation of temporally fixed networks but few quantified the change in network connectivity from disintegration of key features that undergo naturally occurring spatiotemporal dynamics. This is particularly of concern for aquatic systems, which typically show high natural spatiotemporal variability. Here we focused on the Swan Coastal Plain, a bioregion that encompasses a global biodiversity hotspot in Australia with over 1500 water bodies of high biodiversity. Using graph theory, we conducted a temporal analysis of water body connectivity over 13 years of variable climate. We derived large networks of surface water bodies using Landsat data (1999–2011). We generated an ensemble of 278 potential networks at three dispersal distances approximating the maximum dispersal distance of different water dependent organisms. We assessed network connectivity through several network topology metrics and quantified the resilience of the network topology during wet and dry phases. We identified ‘stepping stone’ water bodies across time and compared our networks with theoretical network models with known properties. Results showed a highly dynamic seasonal pattern of variability in network topology metrics. A decline in connectivity over the 13 years was noted with potential negative consequences for species with limited dispersal capacity. The networks described here resemble theoretical scale-free models, also known as ‘rich get richer’ algorithm. The ‘stepping stone’ water bodies are located in the area around the Peel-Harvey Estuary, a Ramsar listed site, and some are located in a national park. Our results describe a powerful approach that can be implemented when assessing the connectivity for a particular organism with known dispersal distance. The approach of identifying the surface water bodies that act as ‘stepping stone’ over time may help prioritize surface water bodies that are essential for maintaining regional scale connectivity.