Spatiotemporal dynamic of surface water bodies using Landsat time-series data from 1999 to 2011
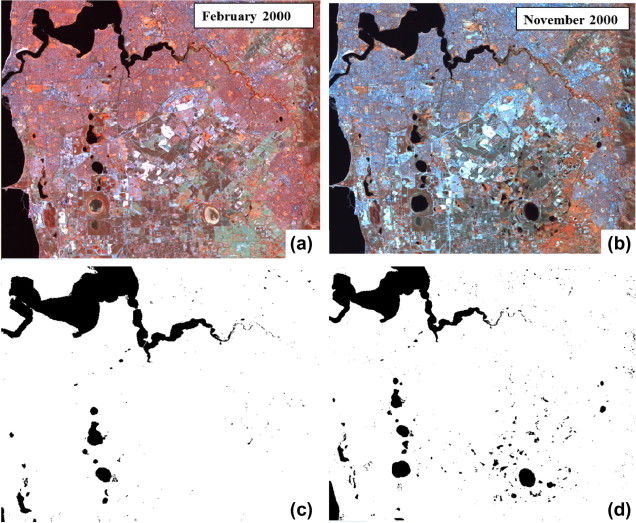 Figure 4 from the publication, “Landsat images (path row 112/082, bands 4, 5, 6 (RGB)) showing the seasonal variability as well as the results of the classification (a) summer season imagery, (b) winter season image, (c) result of the classification for the summer season and (d) result of the classification for the winter season image. Water bodies are shown in black in all images.”
Figure 4 from the publication, “Landsat images (path row 112/082, bands 4, 5, 6 (RGB)) showing the seasonal variability as well as the results of the classification (a) summer season imagery, (b) winter season image, (c) result of the classification for the summer season and (d) result of the classification for the winter season image. Water bodies are shown in black in all images.”Abstract
Detailed information on the spatiotemporal dynamic in surface water bodies is important for quantifying the effects of a drying climate, increased water abstraction and rapid urbanization on wetlands. The Swan Coastal Plain (SCP) with over 1500 wetlands is a global biodiversity hotspot located in the southwest of Western Australia, where more than 70% of the wetlands have been lost since European settlement. SCP is located in an area affected by recent climate change that also experiences rapid urban development and ground water abstraction. Landsat TM and ETM+ imagery from 1999 to 2011 has been used to automatically derive a spatially and temporally explicit time-series of surface water body extent on the SCP. A mapping method based on the Landsat data and a decision tree classification algorithm is described. Two generic classifiers were derived for the Landsat 5 and Landsat 7 data. Several landscape metrics were computed to summarize the intra and interannual patterns of surface water dynamic. Top of the atmosphere (TOA) reflectance of band 5 followed by TOA reflectance of bands 4 and 3 were the explanatory variables most important for mapping surface water bodies. Accuracy assessment yielded an overall classification accuracy of 96%, with 89% producer’s accuracy and 93% user’s accuracy of surface water bodies. The number, mean size, and total area of water bodies showed high seasonal variability with highest numbers in winter and lowest numbers in summer. The number of water bodies in winter increased until 2005 after which a decline can be noted. The lowest numbers occurred in 2010 which coincided with one of the years with the lowest rainfall in the area. Understanding the spatiotemporal dynamic of surface water bodies on the SCP constitutes the basis for understanding the effect of rainfall, water abstraction and urban development on water bodies in a spatially explicit way.