Publications and Presentations
Effects of Climate and Anthropogenic Drivers on Surface Water Area in the Southeastern United States
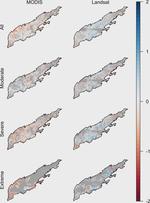
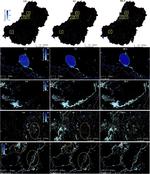
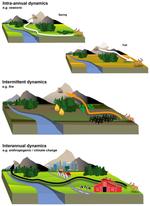
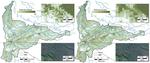
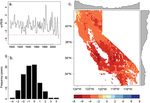
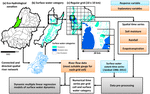
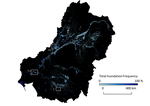
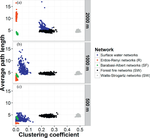
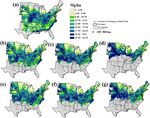
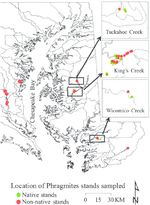
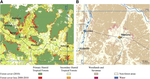
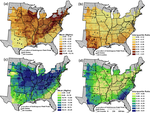
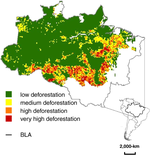
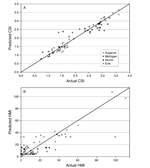
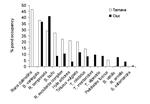
People and the environment rely on water to exist and thrive, especially water on the Earth’s surface because that is the easiest place to get it. The amount of surface water and where it is located is changing with the climate and changes in people’s water use, and our need for it is increasing. To plan ahead for future water needs, we need to better understand how the climate and people are changing surface water patterns both separately and together. To help improve our understanding of these changes, we modeled the amount of surface water in three different ways. First, we modeled based on climate data (like temperature and precipitation); second, based on human data (like land use and population); and third, based on both climate and human data together. We found that we could best model the amount of surface water if we used both climate and human data together, and that human data can explain a lot of the changes in the amount of surface water. These results mean that we can work to control changes in the amount of surface water by controlling human actions through planning and policies.